Nocloud
nocloud specification.Talos supports nocloud data source implementation.
On bare-metal, Talos Linux was tested to correctly parse nocloud configuration from the following providers:
There are two ways to configure Talos server with nocloud platform:
- via SMBIOS “serial number” option
- using CDROM or USB-flash filesystem
Note: This requires the nocloud image which can be downloaded from the Image Factory.
SMBIOS Serial Number
This method requires the network connection to be up (e.g. via DHCP). Configuration is delivered from the HTTP server.
ds=nocloud-net;s=http://10.10.0.1/configs/;h=HOSTNAME
After the network initialization is complete, Talos fetches:
- the machine config from
http://10.10.0.1/configs/user-data - the network config (if available) from
http://10.10.0.1/configs/network-config
SMBIOS: QEMU
Add the following flag to qemu command line when starting a VM:
qemu-system-x86_64 \
...\
-smbios type=1,serial=ds=nocloud-net;s=http://10.10.0.1/configs/
SMBIOS: Proxmox
Set the source machine config through the serial number on Proxmox GUI.
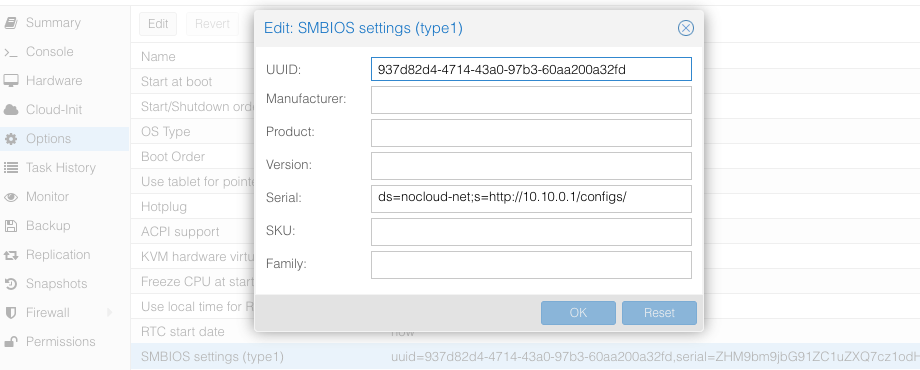
You can read the VM config from a root shell with the command qm config $ID ($ID - VM ID number of virtual machine), you will see something like:
# qm config $ID
...
smbios1: uuid=5b0f7dcf-cfe3-4bf3-87a2-1cad29bd51f9,serial=ZHM9bm9jbG91ZC1uZXQ7cz1odHRwOi8vMTAuMTAuMC4xL2NvbmZpZ3Mv,base64=1
...
Where serial holds the base64-encoded string version of ds=nocloud-net;s=http://10.10.0.1/configs/.
The serial can also be set from a root shell on the Proxmox server:
# qm set $VM --smbios1 "uuid=5b0f7dcf-cfe3-4bf3-87a2-1cad29bd51f9,serial=$(printf '%s' 'ds=nocloud-net;s=http://10.10.0.1/configs/' | base64),base64=1"
update VM 105: -smbios1 uuid=5b0f7dcf-cfe3-4bf3-87a2-1cad29bd51f9,serial=ZHM9bm9jbG91ZC1uZXQ7cz1odHRwOi8vMTAuMTAuMC4xL2NvbmZpZ3Mv,base64=1
Keep in mind that if you set the serial from the command line, you must encode it as base64, and you must include the UUID and any other settings that are already set for the smbios1 option or they will be removed.
CDROM/USB
Talos can also get machine config from local attached storage without any prior network connection being established.
You can provide configs to the server via files on a VFAT or ISO9660 filesystem.
The filesystem volume label must be cidata or CIDATA.
Example: QEMU
Create and prepare Talos machine config:
export CONTROL_PLANE_IP=192.168.1.10
talosctl gen config talos-nocloud https://$CONTROL_PLANE_IP:6443 --output-dir _out
Prepare cloud-init configs:
mkdir -p iso
mv _out/controlplane.yaml iso/user-data
echo "local-hostname: controlplane-1" > iso/meta-data
cat > iso/network-config << EOF
version: 1
config:
- type: physical
name: eth0
mac_address: "52:54:00:12:34:00"
subnets:
- type: static
address: 192.168.1.10
netmask: 255.255.255.0
gateway: 192.168.1.254
EOF
Create cloud-init iso image
cd iso && genisoimage -output cidata.iso -V cidata -r -J user-data meta-data network-config
Start the VM
qemu-system-x86_64 \
...
-cdrom iso/cidata.iso \
...
Example: Proxmox
Proxmox can create cloud-init disk for you. Edit the cloud-init config information in Proxmox as follows, substitute your own information as necessary:
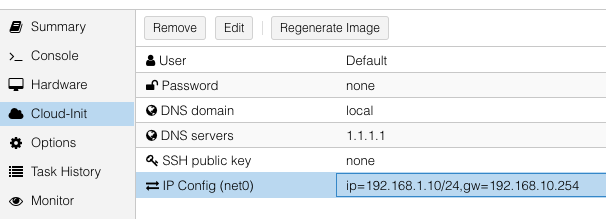
and then add a cicustom param to the virtual machine’s configuration from a root shell:
# qm set 100 --cicustom user=local:snippets/controlplane-1.yml
update VM 100: -cicustom user=local:snippets/controlplane-1.yml
Note:
snippets/controlplane-1.ymlis Talos machine config. It is usually located at/var/lib/vz/snippets/controlplane-1.yml. This file must be placed to this path manually, as Proxmox does not support snippet uploading via API/GUI.
Click on Regenerate Image button after the above changes are made.